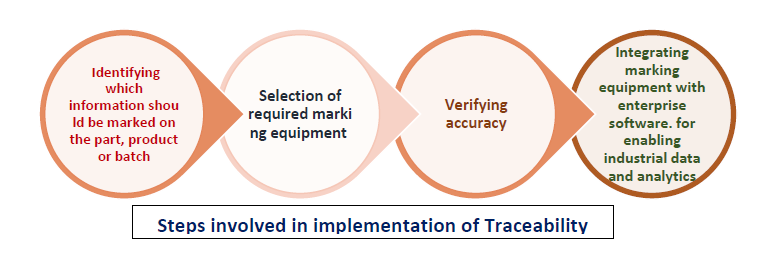
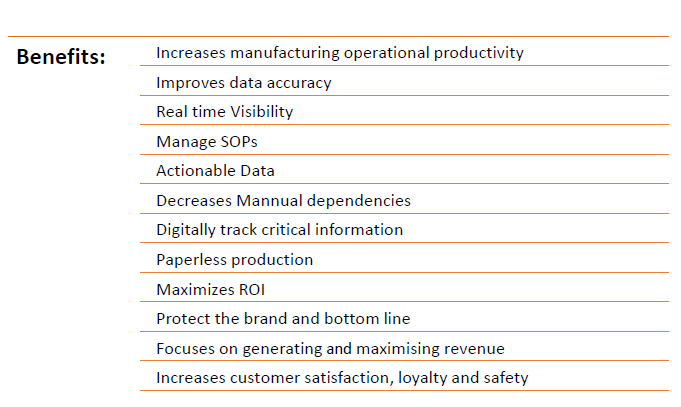
An Ability to Track and Trace : Traceability
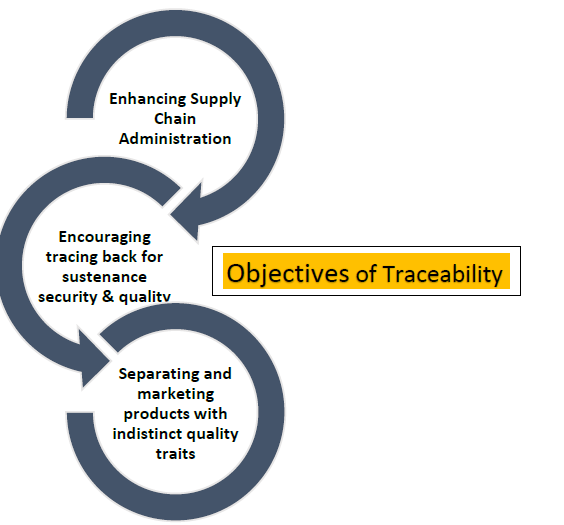
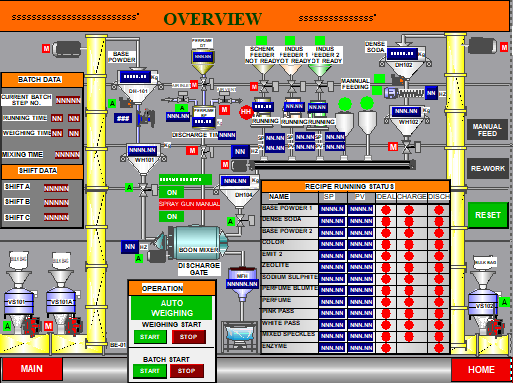
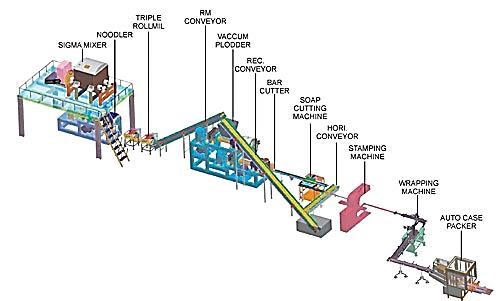
Traceability is the ability of a system to track and trace the every single part, product or batch through the complete manufacturing process. It starts from the movement when a raw material is entered into the manufacturing unit/ factory to the movement a final and finished product is ready for shipping.
This process of Traceability helps/allows the manufacturing units to digitally connect their each and every single part, product or batch to the Sub-assembly, the Main assembly and finally to the Final assembly. This is required and very much in need of the industries to maintain their products quality to save their brand image along with the sustenance in the markets competitive environment and to gather Customers Loyalty.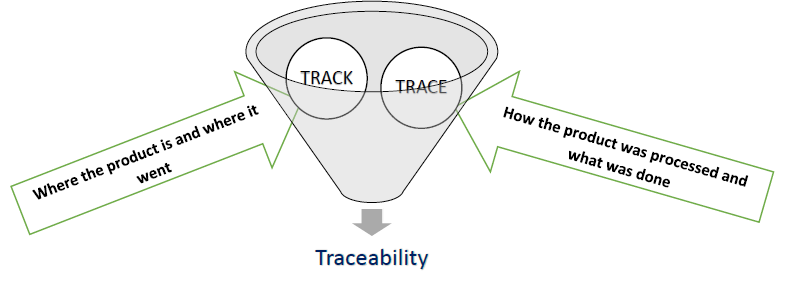
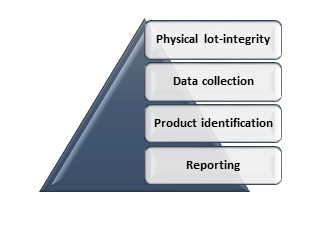
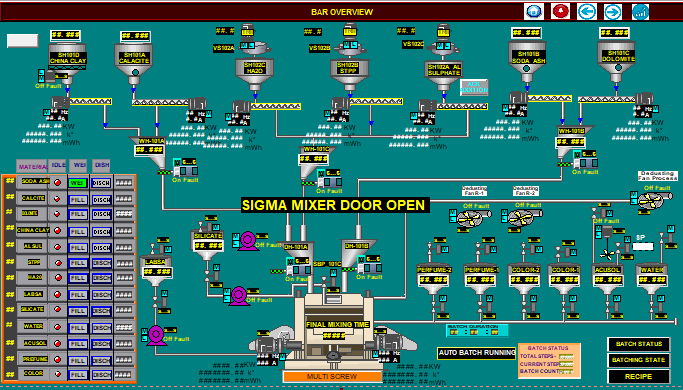
In Manufacturing Traceability systems are found in both part and batch production. There are four elements connected to the design of a lot-tracing system or batch-tracing-system:
- Physical lot-integrity – This refers to the size of the batch of raw material and how good the integrity of the considered batch is maintained. This will determine the the perfection of the traceability solution considered.
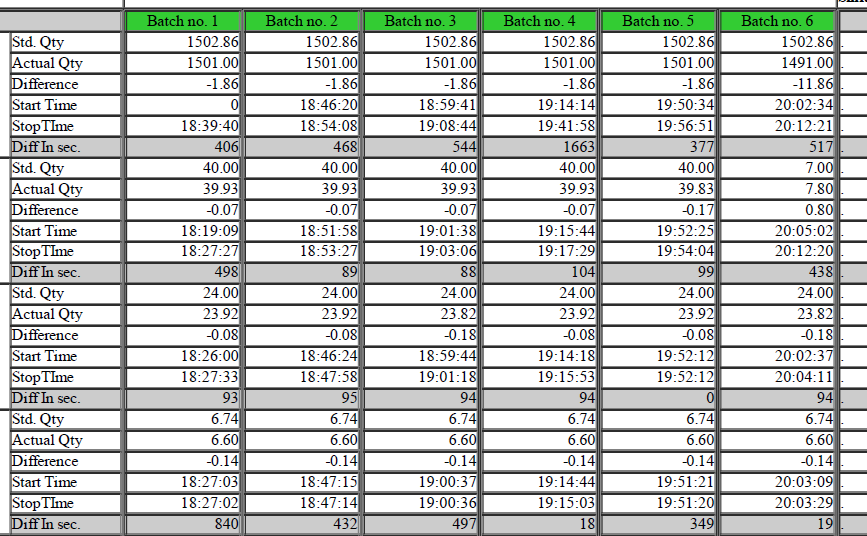
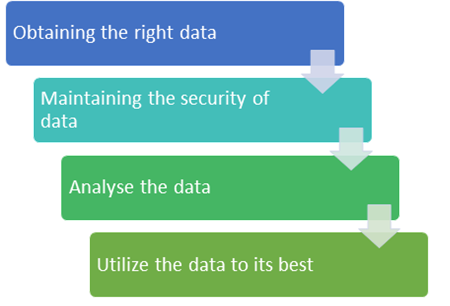
- Data collection – For Data collection there is requirement of Two types of data. One is Process data which will provide the process information and second is Lot-tracing data that will provide the information related to the movement of product batches.
- Product identification – This refers to the connection of identified product data and process data.
- Reporting – It is the use of generated data and visualization of same .